Energy Profile Diagram Of E1 Reaction
What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate E1 reaction elimination unimolecular Energy e1 reaction potential coordinate diagrams sodium bromobutane following which represents transcribed text show hydroxide
Elimination reaction : E1 and E2 reaction – Examples, Mechanism
Solved 13. which of the following potential energy diagrams Free energy diagrams help free students from memorization – teach the Energy reactions profiles reaction profile intermediate intermediates shows chemistry stability chemguide activation reactants into conversion barriers temporary however
Energy diagrams diagram memorization students help mechanism figure
Elimination unimolecular e1 reactionElimination reaction : e1 and e2 reaction – examples, mechanism Sn2 sn1 kinetics reactivity stereochemistry sn alkyl towards halidesA look at energy profiles for reactions.
A look at energy profiles for reactionsE2 elimination reactivity Transition intermediate coordinate chemistryE1 dehydrohalogenation.

Sn1 and sn2 reaction – kinetics, mechanism, stereochemistry and reactivity.
E1 reactionElimination reaction : e1 and e2 reaction – examples, mechanism Coordinate elimination mechanism e1cb activation unimolecular conjugate δeEnergy sn1 diagram profile reaction mechanism draw labelled neat shaalaa reactions exam chemistry 12th hsc science general board.
Energy reactions reaction activation profiles look profile exothermic chemistry changes reverse chemical endothermic simple level catalyzed forward catalysed below chemMechanism elimination reactivity Draw a neat, labelled energy profile diagram for sn1 reaction mechanismElimination halides nucleophilic substitution alkyl wade sn1 reactions carbocation.

E1cb
.
.


Draw a Neat, Labelled Energy Profile Diagram for Sn1 Reaction Mechanism

06 - Alkyl Halides ,Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination - Wade

Elimination reaction : E1 and E2 reaction – Examples, Mechanism

What is the Difference Between a Transition State and an Intermediate

E1cB - Elimination (Unimolecular) Conjugate Base
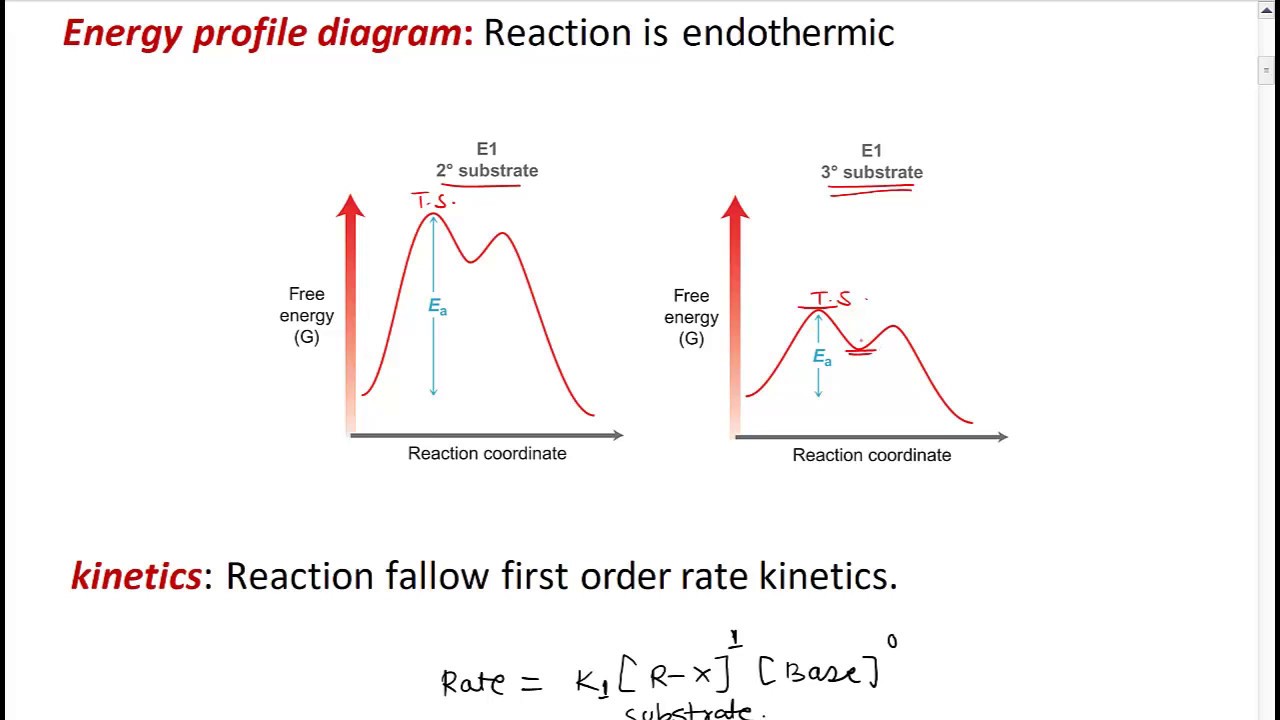
Elimination unimolecular E1 reaction - YouTube

Free Energy Diagrams Help Free Students from Memorization – Teach the

Solved 13. Which of the following potential energy diagrams | Chegg.com

Elimination reaction : E1 and E2 reaction – Examples, Mechanism